CFD Explosion Study
The methodology adopted for the determination of explosion overpressure and the frequency with which any overpressure value is likely to be exceeded, can be described in the following three distinct steps:
- Determination of the flammable gas cloud size distribution from an accidental release from a range of hole sizes, locations, release directions, wind directions and wind speeds.
- Simulation of the explosions for a range of gas clouds sizes for a number of ignition locations with gas clouds located in various regions.
- Derivation of the exceedance curves using the frequency of releases, the probability distribution of flammable gas cloud sizes, ignition probabilities, and the results of explosion simulations.
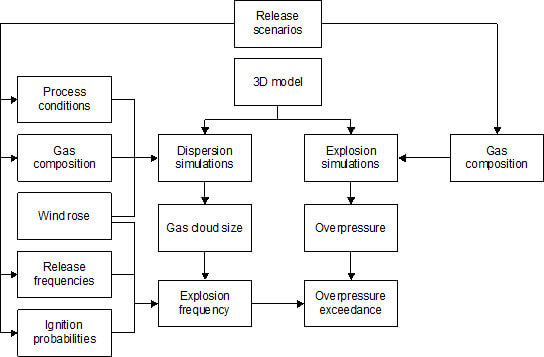
CFD Modelling Flow Chart
The premise of the procedure is based on estimating the most probable explosion load and not a worst case, but in such a way that when simplifications are made according to an assumed idealistic model, the total risk picture, load or response, should not be too low, but rather be on the conservative side.
CFD Explosion Study
The methodology adopted for the determination of explosion overpressure and the frequency with which any overpressure value is likely to be exceeded, can be described in the following three distinct steps:
- Determination of the flammable gas cloud size distribution from an accidental release from a range of hole sizes, locations, release directions, wind directions and wind speeds.
- Simulation of the explosions for a range of gas clouds sizes for a number of ignition locations with gas clouds located in various regions.
- Derivation of the exceedance curves using the frequency of releases, the probability distribution of flammable gas cloud sizes, ignition probabilities, and the results of explosion simulations.
CFD Modelling Flow Chart
The premise of the procedure is based on estimating the most probable explosion load and not a worst case, but in such a way that when simplifications are made according to an assumed idealistic model, the total risk picture, load or response, should not be too low, but rather be on the conservative side.